The value of a man should be seen in what he gives and not in what he is able to receive.
Albert Einstein
The value of a man should be seen in what he gives and not in what he is able to receive.
Albert Einstein
Over the last 50 years, CETAL has built an extensive experience on heating elements, heat exchange and associated technologies.
The purpose of CETALpedia is to provide access to the key information when it comes to:
In any case, do not hesitate to contact our CETAL engineers and experts to find the best solutions for your project.
| Substance | Density (kg/dm³) | Specific Heat (kcal/kg°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Acetic Acid | 1,05 | 0,522 |
| Acetone | 0,79 | 0,514 |
| Allyl Alcohol | 0,85 | 0,665 |
| Ammonia | 0,70 | 1,099 |
| Amyl Alcohol | 0,82 | 0,65 |
| Aniline | 1,02 | 0,512 |
| Bromine | 3,12 | 0,107 |
| Butyl Alcohol | 0,81 | 0,563 |
| Butyric Acid | 0,96 | 0,515 |
| Carbolic Acid (Phenol) | 1,07 | 0,561 |
| Carbon Disulfide | 1,26 | 0,24 |
| Carbon Tetrachloride | 1,59 | 0,201 |
| Caustic Soda (50% Solution) | 1,53 | 0,78 |
| Decane Ether | 0,73 | 0,5 |
| Di-ethyl | 0,71 | 0,541 |
| Ether | 0,74 | 0,503 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 0,84 | 0,468 |
| Ethyl Alcohol | 0,79 | 0,68 |
| Ethyl Bromide | 1,45 | 0,215 |
| Ethyl Chloride | 0,90 | 0,368 |
| Ethyl Iodide | 1,93 | 0,161 |
| Ethylene Glycol | 1,11 | 0,555 |
| Ethylene Bromide | 2,19 | 0,173 |
| Ethylene Chloride | 1,15 | 0,294 |
| Formic Acid | 1,22 | 0,526 |
| Glycerin | 1,26 | 0,576 |
| Heat Transfer Fluids | ||
| Dowtherm A | 1,06 | 0,377 |
| Dowtherm G | 1,05 | 0,377 |
| Mobiltherm 603 | 0,86 | 0,592 |
| Therminol VP-1 | 1,06 | 0,377 |
| Heptane | 0,68 | 0,532 |
| Hexane | 0,66 | 0,6 |
| Linseed Oil | 0,93 | 0,44 |
| Methyl Acetate | 0,93 | 0,468 |
| Methyl Alcohol | 0,79 | 0,601 |
| Methyl Iodide | 2,28 | — |
| Nitric Acid -100% | 1,51 | 0,42 |
| Nitrobenzene | 1,21 | 0,35 |
| Octane | 0,71 | 0,51 |
| Olive Oil | 0,92 | 0,471 |
| Pentane | 0,63 | 0,558 |
| Petroleum Products | 0,00 | 0 |
| Asphalt | 1,00 | 0,42 |
| Benzene (Benzol) | 0,88 | 0,412 |
| Kerosene | 0,80 | 0,5 |
| Fuel Oil #6 | 0,94 | 0,41 |
| Gasoline | 0,66 | 0,5 |
| Lube Oils | 0,89 | 0,43 |
| Naphthalene | 1,14 | 0,4 |
| Paraffin (Melted) | 0,71 | 0,71 |
| Toluene | 0,87 | 0,404 |
| Propionic Acid | 0,99 | 0,473 |
| Propyl Alcohol | 0,80 | 0,57 |
| Soy Bean Oil | 0,92 | 0,28 |
| Sulfur (Melted) | 0,23 | 0,234 |
| Sulfuric Acid -100% | 1,83 | 0,344 |
| Tallow (Lard) | 0,94 | 0,64 |
| Turpentine | 0,87 | 0,42 |
| Water | 1,00 | 1 |
| Xylene (Ortho) | 0,88 | 0,411 |
| Substance | Density (kg/m³) | Specific Heat (kcal/kg°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Acetylene | 1,17 | 0,38 |
| Air | 1,29 | 0,24 |
| Ammonia | 0,83 | 0,52 |
| Argon | 1,78 | 0,12 |
| Butane-iso | 2,76 | — |
| Butane-n | 2,59 | — |
| Carbon Dioxide | 1,97 | 0,20 |
| Carbon Monoxide | 1,25 | 0,24 |
| Chlorine | 3,20 | 0,11 |
| Chlorodifl uoromethane (F-22) | 4,98 | 0,15 |
| Chloroform | 0,14 | |
| Cyanogen | 2,41 | 0,41 |
| Dichlorodifl uoromethane (F-22) | 5,67 | 0,14 |
| Ethane | 1,45 | 0,39 |
| Ethyl Chloride | 3,09 | 0,28 |
| Ethylene | 1,35 | 0,40 |
| Fluorine | 1,83 | 0,18 |
| Helium | 0,18 | 1,25 |
| Hydrogen | 0,10 | 3,41 |
| Hydrogen Bromide | 3,92 | 0,08 |
| Hydrogen Chloride | 1,76 | 0,19 |
| Hydrogen Fluoride | 0,92 | — |
| Hydrogen Iodide | 6,12 | 0,06 |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | 1,66 | 0,25 |
| Methane | 0,77 | 0,59 |
| Methyl Chloride | 2,45 | 0,24 |
| Methyl Ether | 2,26 | — |
| Methyl Fluoride | 1,66 | — |
| Neon | 0,97 | — |
| Nitric Oxide | 1,34 | 0,23 |
| Nitrogen | 1,26 | 0,24 |
| Nitrous Oxide | 2,12 | 0,21 |
| Oxygen | 1,43 | 0,22 |
| Phosphine | 1,64 | — |
| Propane | 2,17 | — |
| Silicone Tetrafl uoride | 5,04 | — |
| Sulfur Dioxide | 2,86 | 0,15 |
| Water Vapor | 0,64 | 0,48 |
| Xenon | 6,29 | — |
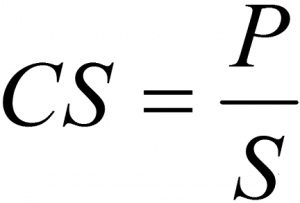
P = Power in W
S = Surface in cm²
CS = watt density in en W/cm²
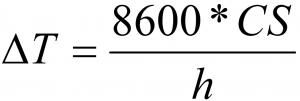
ΔT = T°C gap between tube sheath and medium in °C
CS = watt density in en W/cm²
h = heat exchange coefficient in kcal/h*m²*°C
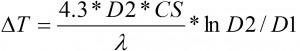
ΔT = T°C gap between wire and tube sheath in °C
P = Power from D1 to D2 in kW
D1 and D2 internal and external diameter
λ = conduction coefficient in kcal/h*m*°C
L = cylinder length in m
CETAL engineers and expert define the watt density through an heat exchange software allowing to take into account all parameters.
CETAL software can effect detailed heat exchange calculations, the key outputs are:
For basic design, please find below some references sorted by fluids.
Inputs
|
Outputs
|
|
Issues |
Solutions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic maintenance actions to be taken are: